10th CBSE - Regular Batch

One of the most important years in every CBSE student’s life is 10th CBSE. The students have to be well organized, determined and they must get expert’s guidance to score his best in the Class 10 Board Examinations.
- This is the yearlong course which covers all major subjects
- India’s best faculties are involved in every subject.
- Subjective papers with evaluation will make every student successful.
- Top quality visuals are used for concept building and subject mastery.
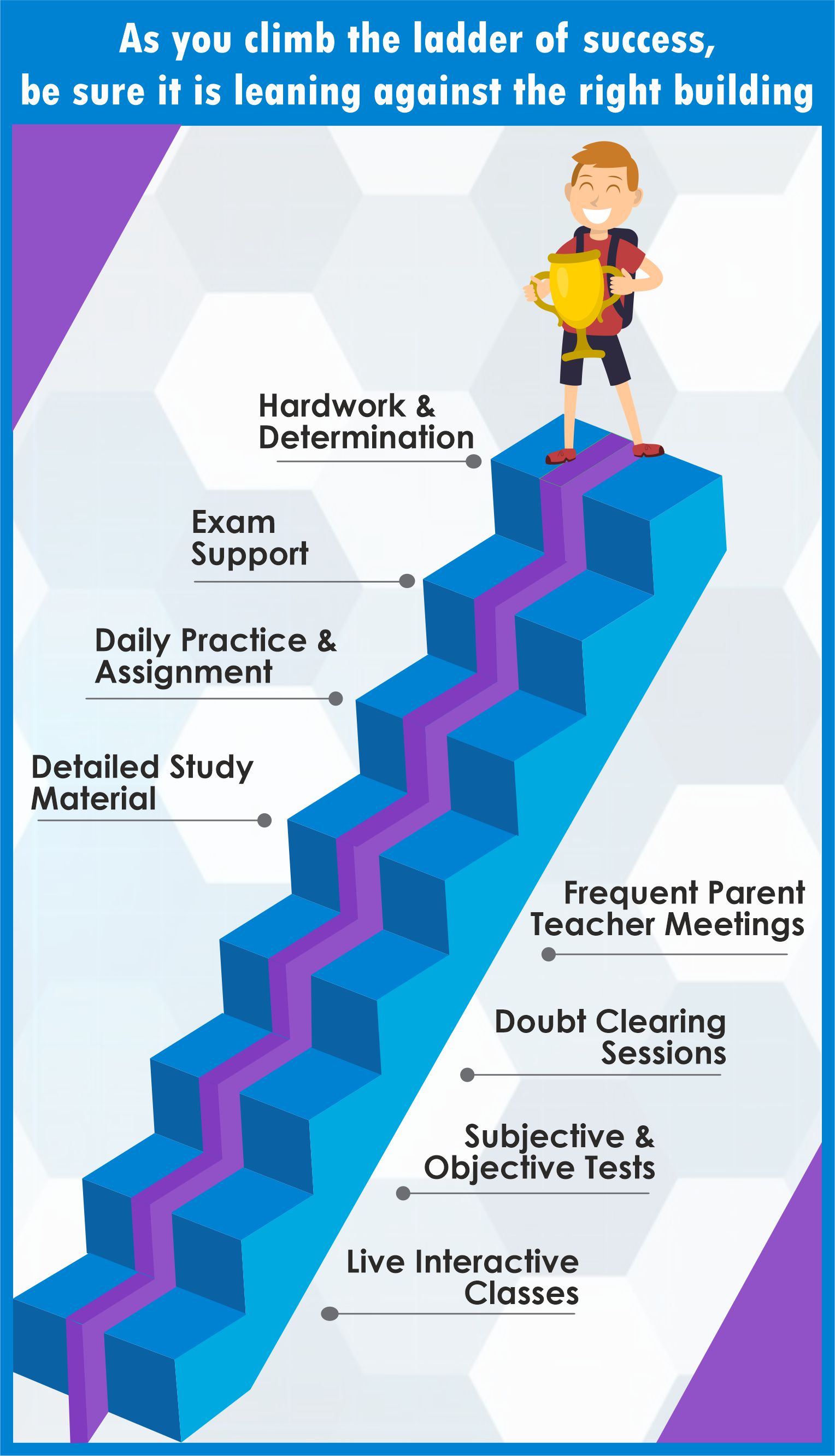
How the course is shaped.
- Live Interactive Classes
- Subjective and objective tests
- Periodic doubt clearing
- Parents-Teacher meetings
- Study material in hard copies.
- Support till exam
- Daily practice assignments (DPA)
Assignment and homework help students with their studies. It also helps in getting the preparation done for exams. Our teachers flash the assignments before the lecture starts so that students remain focused throughout the class.
-
Daily practice assignments (DPA) are provided on student’s dashboard
-
Solutions are uploaded on the dash board in three days.
-
It helps our students remain exam focused.
At Tutoratti, we have multiple test types
- Chapter tests
- Cumulative tests
- Semi Prelims
- Full Prelims
Every paper is evaluated by experts and all the checked papers can be accessed easily on the student’s dashboard. And yes, model answers are also provided.
Why tests are such an important element of our courses?
- Practice tests give ideas about which topics mastered and motivates them to focus on weak areas.
- Practice test is a feed back to our teachers.
- Practice tests stimulate revision and studying and it improves retention.
- Practice tests reduces test anxiety.
- Writing practice tests improves learning as well as final exam outcome.
For Class
-
10th
Subjects Covered
-
Physics
-
Chemistry
-
Mathematics
-
Biology
-
English
-
Social Science













 ICSE 10 - 2023 - 2024
ICSE 10 - 2023 - 2024
 Test Series - 10th SSC
Test Series - 10th SSC
 Test Series - 10th CBSE
Test Series - 10th CBSE
 9th ICSE - Regular Batch
9th ICSE - Regular Batch
 Test Series - 10th ICSE
Test Series - 10th ICSE



